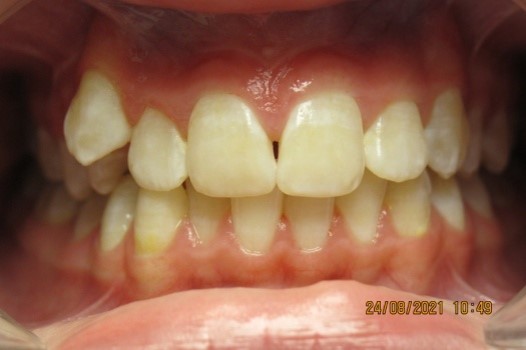
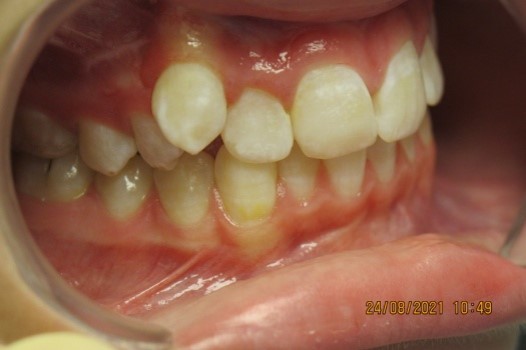
Vestibular teeth position
This anomaly is characterized by the
location of the tooth outside the dentition in the vestibule of the oral cavity.
On the upper jaw, as a rule, above the dentition, on the lower jaw - below the
dentition. Of the lateral teeth, the first premolars and second molars can have
a vestibular position. Most often, canines are located on the vestibular side
(because until they are completely erupted, they pass a long gap from the lower
edge of the orbit, and on the lower jaw - from the floor of the oral cavity to
the alveolar process).
Etiology,
pathogenesis:
- heredity;
- harmful habits of sucking a thamb,
pencil, pen or other objects;
- oral or mixed breathing,
swallowing, speech, lip closure, leading to underdevelopment of the
jaws;
115
- disproportionate of the teeth and
jaw size;
- delayed physiological change of
temporary teeth;
- trauma of the teeth, alveolar
process, jaws;
- macrodentia (absolute or
individual);
- presence of supernumerary
tooth;
- violation of the tooth follicle
formation;
- micrognathia of the
jaw;
- mesial displacement of teeth
surrounding anomalous tooth;
- premature removal of temporary
teeth without preventive measures;
- narrowing and shortening of the
dentition and apical base of varying degrees;
- mismatch of the width of the
dentition and apical base.
Functional disorders:
- speech
disorder;
- biting
of food;
-
impaired lip closure;
-
periodontal tissue diseases (localized, generalized).
Aesthetic changes:
-
visualization of an abnormally positioned tooth during talking and
smiling.
Forms of
anomaly:
- with space in the dentition;
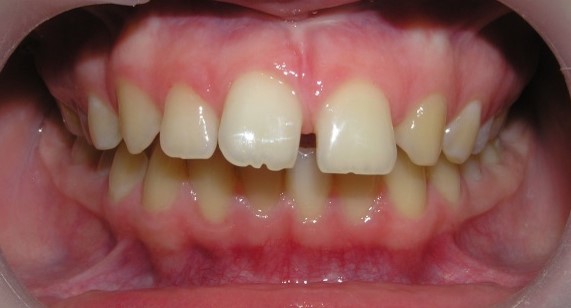
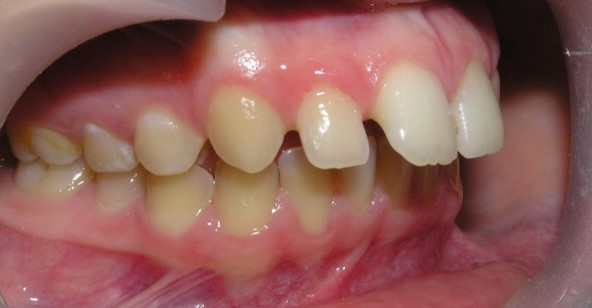
- without space in the dentition;
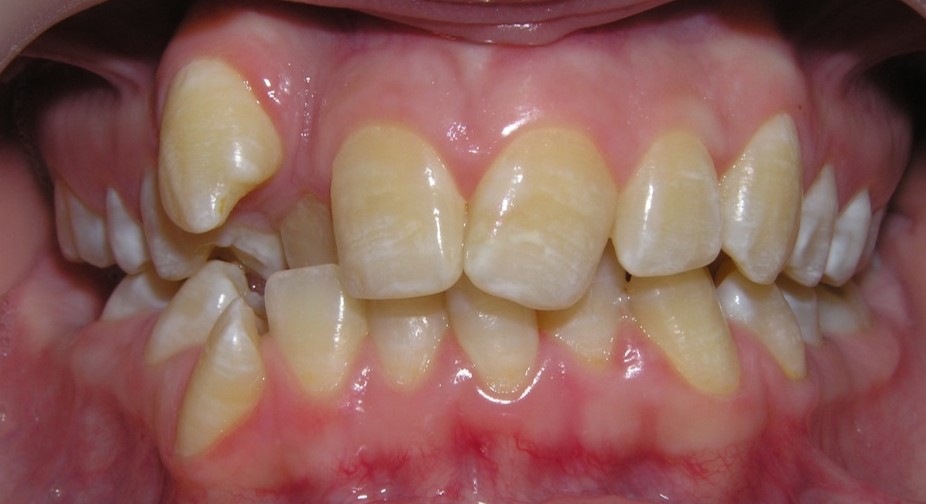
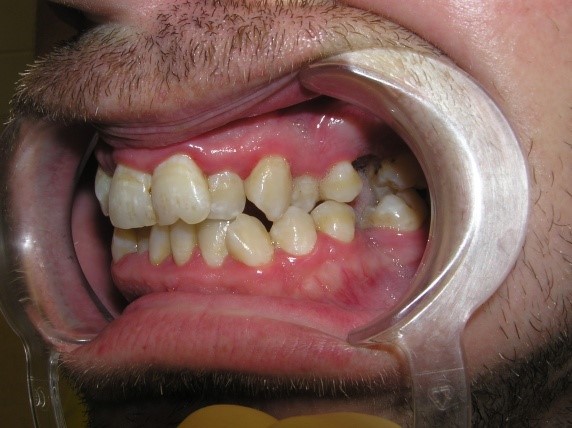
- with concomitant anomalies of the dentition and bite;
- with compensated space deficiency of dentition;
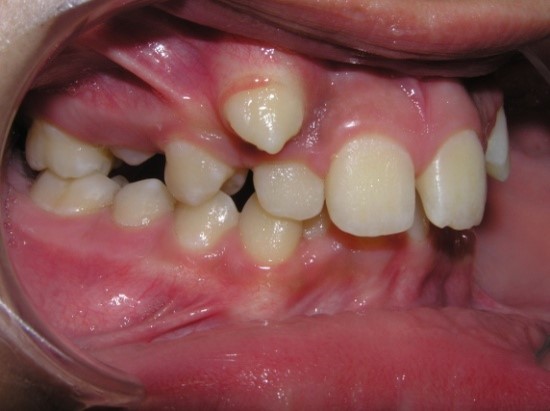
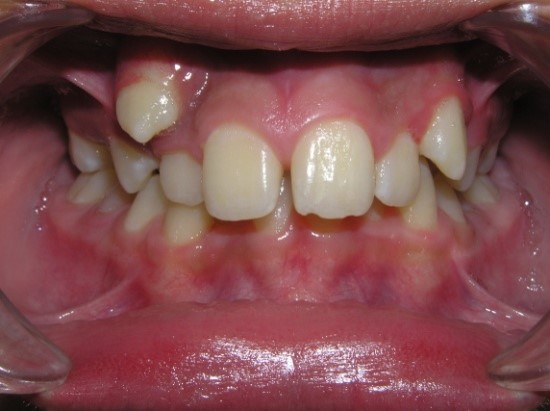
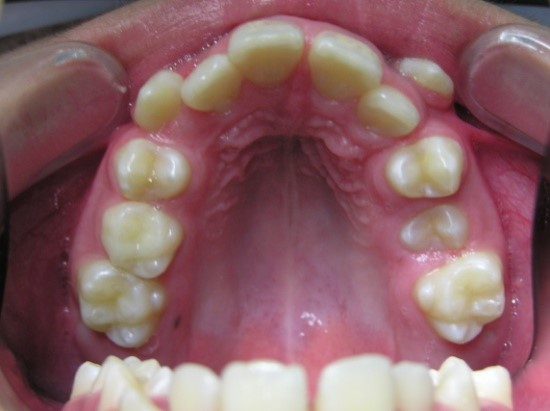
- with decompensated or complete space deficiency of dentition.
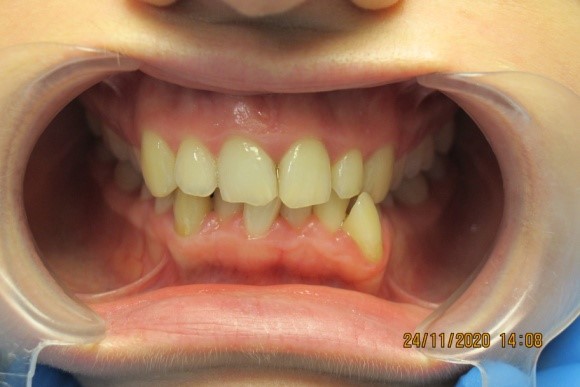
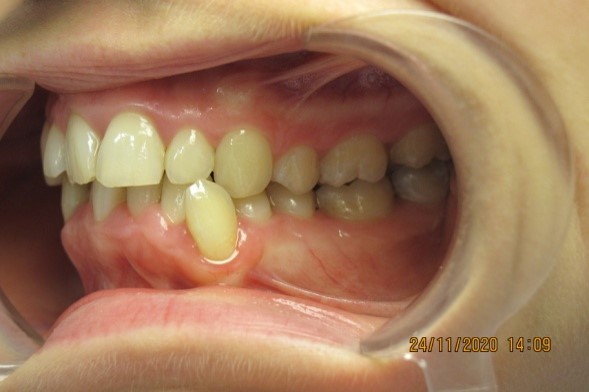
Examination methods:
1.
Clinical.
2.
Paraclinical.
X-ray:
-
orthopantomography;
-
computer tomography.
Biometric:
- dental
examination by methods:
Tonn
Bolton
Pont and
H. Linder, G. Hart
Korkhaus
Snagina
Little
Nance
Schwarz
Fuss
Schmuth
Facial
photometry.
Reopardodontography.
Principles of
treatment:
Preparatory period
-
psychotherapeutic preparation;
-
elimination of the risk factor (if it possible);
-
elimination of the etiological factor (if it possible);
-
sanitation of the oral cavity;
-
checking the state of oral hygiene, if necessary -
training;
-
prosthetic preparation (according to indications);
-
surgical preparation (according to indications).
Active
period of orthodontic treatment in temporary and mixed
dentition:
-
functional methods of treatment (myogymnastics, massage,
etc.);
-
appliances method of treatment taking into account the clinical situation of the
malocclusion (creation of space in the dental arch for an abnormally located
tooth: expansion of the dentition, lengthening of the dentition, distalization
of teeth, etc.);
-
normalization of functions (aesthetic, speech, chewing);
-
surgical treatment methods (serial sequential extraction of teeth by Hotz;
extraction of individual teeth; extraction of supernumerary tooth,
etc.);
-
stripping.
Active period of orthodontic
treatment in permanent dentition:
- appliances treatment method taking
into account the clinical situation
of the malocclusion
(creation of space in the dental arch for an abnormally located tooth: expansion
of the dentition, lengthening of the dentition, distalization of teeth,
etc.);
- normalization of functions
(aesthetic, speech, chewing).
- surgical treatment methods (extraction of individual teeth;
supernumerary tooth, compact osteotomy, insert of orthodontic implants,
etc.).
- stripping;
- prosthetic
treatment;
- functional treatment methods
(myogymnastics, massage, etc.);
- physiotherapeutic treatment
methods: vacuum therapy, low-frequency therapeutic vibration, MRI-magnetic
resonance reflexotherapy, electrophoresis, ultrasound, ultraphonophoresis,
etc.
Retention
period of orthodontic treatment
- preservation of the achieved
result and prevention of relapse with the help of special equipment - retainers
(fixed, removable);
- functional adaptation to the newly
created occlusion;
- extraction of the rudiments of third
molars (if necessary).