Tortoocclusion of teeth (rotation)
Tortoocclusion of teeth (syn. –
tortoanomaly, tooth rotation around the axis) is observed, more often in
permanent occlusion and less often in temporary occlusion. More often than other
teeth, the incisors of the upper and lower jaws rotate along the axis, less
often – canines, premolars and molars. The rotation of the tooth can be
insignificant (from 14ᵒ to 45ᵒ) and significant (from 90ᵒ to 180ᵒ).
Tortoocclusion of a tooth can be combined with other pathological occlusions of
the same tooth.
.
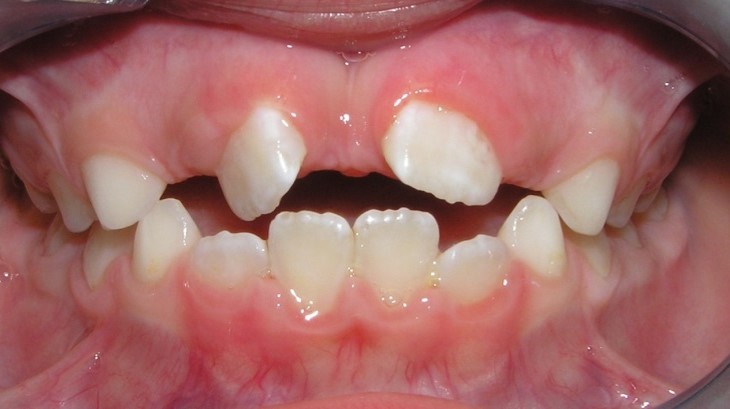
Pic.20. Tortoocclusion of teeth 11 and 21.
Etiology,
pathogenesis:
- heredity;
- harmful habits of biting cheeks,
lips;
- impaired breathing, speech,
closing of lips, which leads to underdevelopment of the
jaws;
- impaired formation of the tooth
root or alveolar process;
- the presence of impacted
teeth;
- disorder of the tooth germ
position;
- sports (when the patient uses the
wrong breathing technique);
- ENT
diseases;
- discrepancy in the size of the
teeth and jaws;
- delayed physiological change of
temporary teeth;
- trauma to the teeth, alveolar
process, jaws;
- macrodentia (absolute or
individual);
- presence of supernumerary
tooth;
- disorder of the tooth
formation;
- micrognathia of the
jaw;
- premature extraction of temporary
molars without preventive measures;
- narrowing and shortening of the
dentition and apical base of varying degrees;
- discrepancy in the width of the
dentition and apical base;
- violation of calcium-phosphorus
metabolism;
- vitamin D deficiency
states.
Functional disorders:
-
breathing;
-
speech;
-
chewing;
-
impaired lip closure;
-
chronic trauma to the mucous membrane of the lip;
-
dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
-
periodontal tissue diseases (localized, generalized).
Aesthetic changes:
-
half-open mouth;
-
visualization of anomalous tooth during talking and
smiling;
- deep
supramental fold;
-
smoothed nasolabial folds;
-
disorder of facial proportions;
-
disorder of facial symmetry.
Forms of anomaly:
- with space in the dentition;
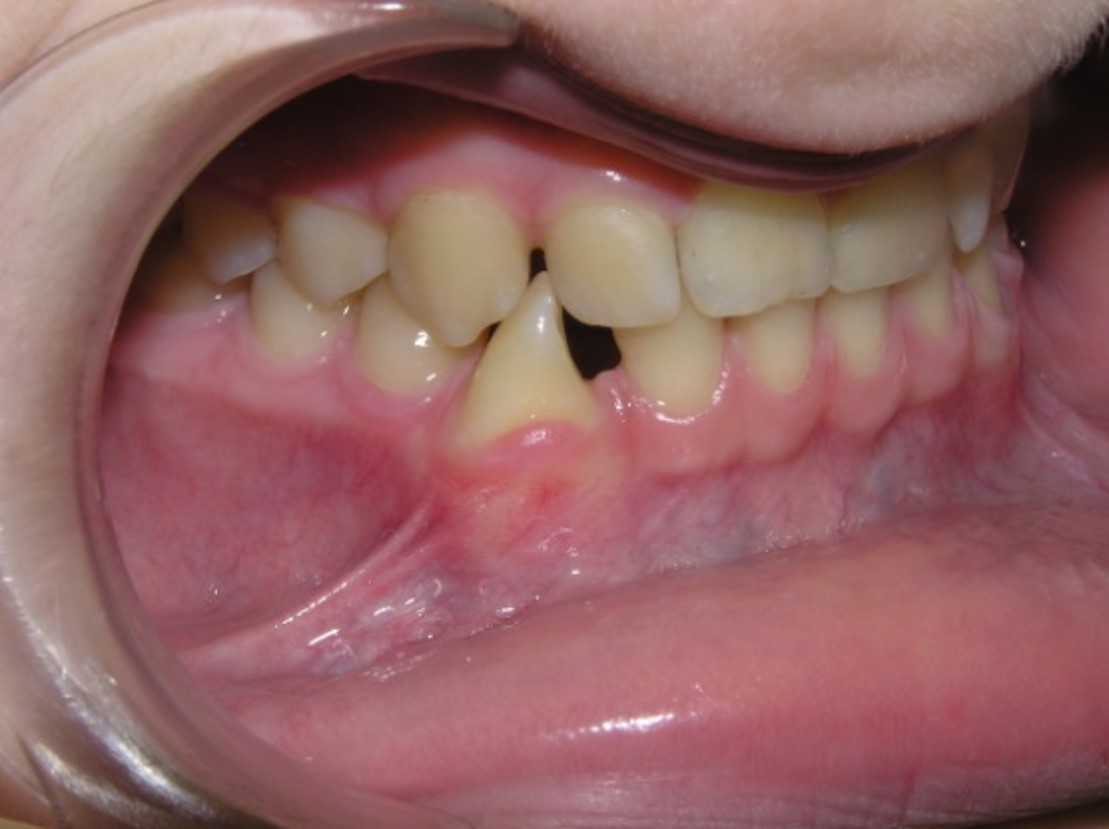
- without space in the dentition;
- with concomitant anomalies of the
dentition and bite;
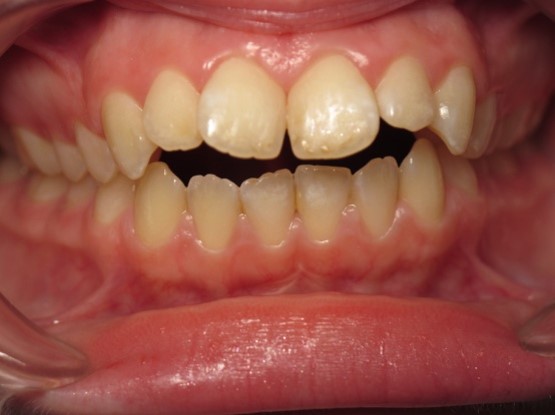
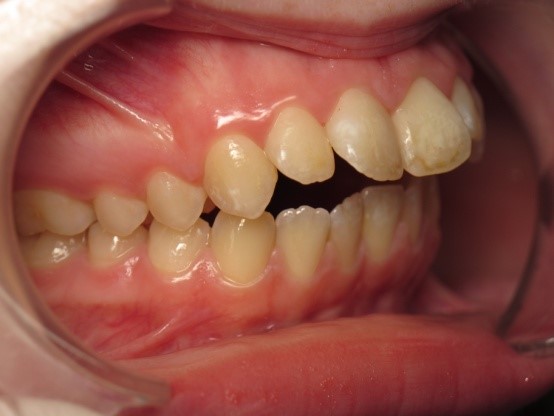
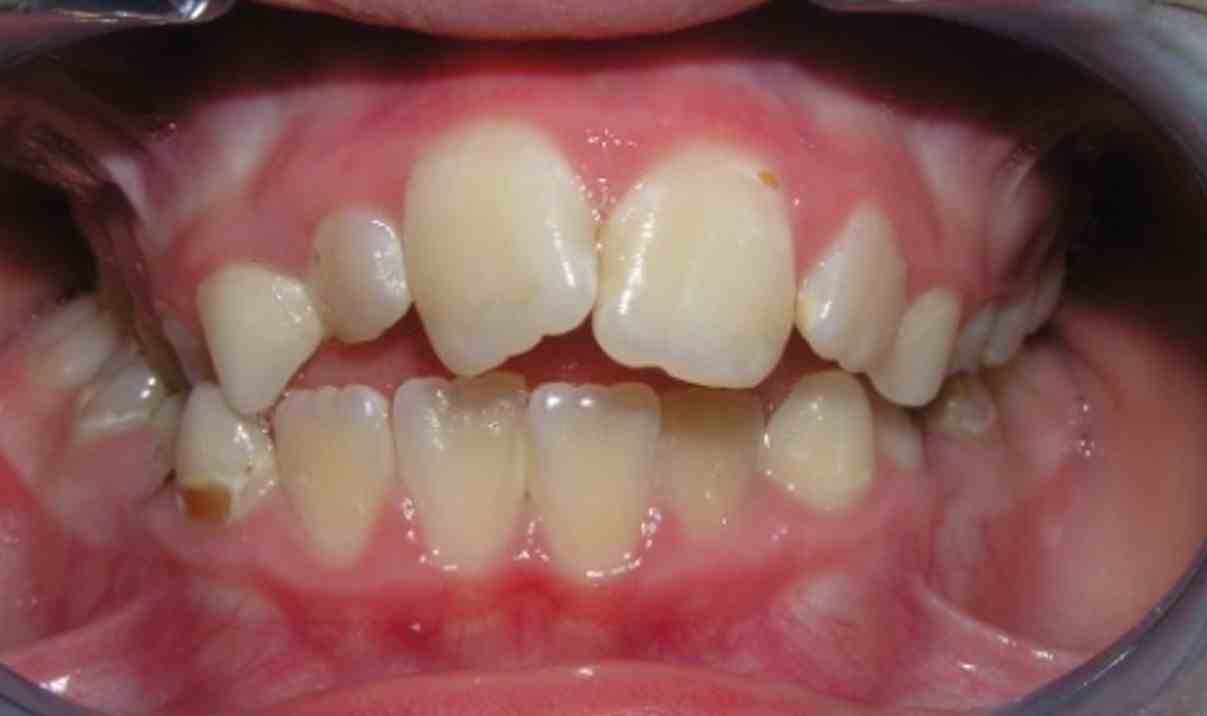
Pic.22. Tortoocclusion of teeth 11 and 21, open bite.
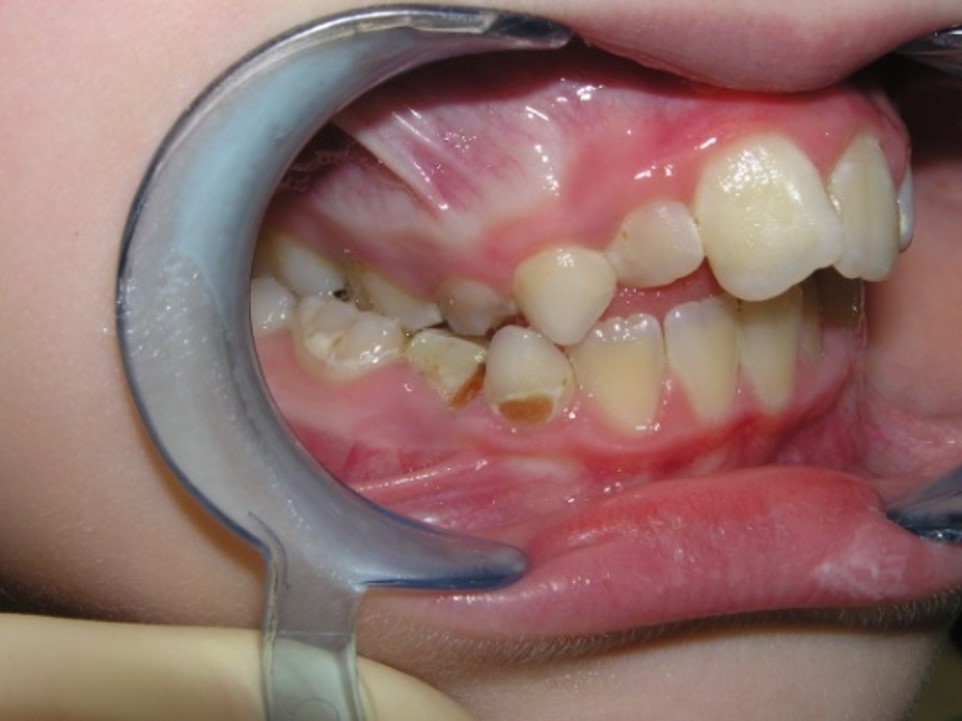
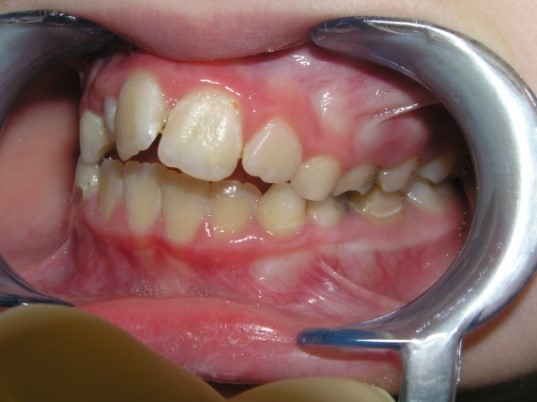
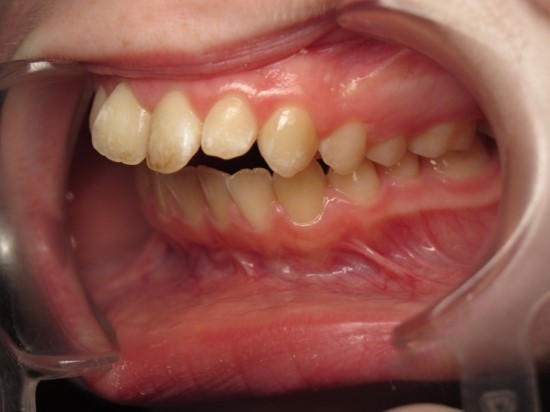
Pic.23. Tortoocclusion of teeth 11 and 21, prognathic, cross bite.
- with compensated deficiency of
space in the dentition;
- with decompensated or complete
deficiency of space in the dentition.
Research methods:
1.
Clinical.
2.
Paraclinical.
X-ray:
-
orthopantomography;
-
computer tomography.
Biometric:
- dental
examination by methods:
Tonn
Bolton
Pont and
H. Linder, G. Hart
Korkhaus
Snagina
Little
Nance
Schwarz
Fuss
Schmuth
Facial
photometry.
Reopardodontography.
Principles of
treatment:
Preparatory period
-
psychotherapeutic preparation;
-
elimination of the risk factor (if possible);
-
elimination of the etiological factor (if possible);
- oral
cavity sanitation;
-
checking the state of oral hygiene, if necessary -
training;
-
prosthetic preparation (according to indications);
-
surgical preparation (according to indications).
Active
period of orthodontic treatment in temporary and mixed
occlusion:
- functional treatment methods
(myogymnastics, massage, etc.);
- appliances treatment method taking
into account the clinical manifestation of the pathology (creation of space in
the dental arch for an abnormally located tooth: expansion of the dentition,
lengthening of the dentition, distalization of the teeth,
etc.);
- normalization of functions
(aesthetic, speech, chewing);
- normalization of the bite height
(if necessary);
- surgical treatment methods (serial
sequential extraction of teeth according to Hotz; extraction of individual
teeth; extraction of supernumerary tooth, etc.);
- separation of the bite by using a
bite plate, occlusal overlays;
- stripping.
Active
period of orthodontic treatment in permanent
occlusion:
- appliances treatment method taking
into account the clinical manifestation of the pathology (creation of space in
the dental arch for an abnormally located tooth: expansion of the dentition,
lengthening of the dentition, distalization of the teeth, etc.);
- normalization of functions
(aesthetic, speech, chewing).
- surgical treatment methods
(extraction of individual teeth; supernumerary tooth, compact osteotomy, insert
of orthodontic implants, etc.).
- stripping;
- prosthetic
treatment;
- separation of the bite by using a
bite plate, occlusal overlays;
- functional treatment methods
(myogymnastics, massage, etc.);
- physiotherapeutic treatment
method: vacuum therapy, low-frequency therapeutic vibration, MRI-magnetic
resonance reflexotherapy, ultraphonophoresis, ultrasound, electrophoresis,
etc.
Retention
period of orthodontic treatment:
- preservation of the achieved
result and prevention of relapse with the help of special equipment - retainers
(fixed, removable);
- functional adaptation to the newly
created occlusion;
- extraction of the rudiments of
third molars (if necessary).