Teeth transposition
Transposition of
teeth is a rare anomaly, the frequency of which is approximately 0.6% and is
characterized by the fact that individual teeth change places. For example, a
canine is in the place of a premolar, and a premolar in the place of a canine.
Cases of eruption of a canine between premolars, and permanent lateral incisors
– distal to the deciduous canines, which occurs as a result of premature loss of
deciduous molars, have been described. The upper canines are more often involved
in the process of transposition, especially in combination with the first
premolars.
Incorrect eruption
of a canine, which leads to impaction, is most often due to lack of space. But
sometimes the rudiment of a canine erupts in a dystopian position, which is
accompanied by transposition, even if there is free space. Most often, there is
a unilateral transposition and more often on the left
side.
Etiology,
pathogenesis:
- heredity;
- transposition of rudiments in the
process of dentinogenesis;
- movement of teeth during
eruption;
- ankylosis of milk
teeth;
- delay in physiological change of
temporary teeth;
- trauma of teeth, alveolar process,
jaws;
- disorder of the tooth
formation.
Functional
disorders:
- biting off
food.
Aesthetic
changes:
- visualization of an abnormally
located tooth during talking and smiling.
Forms of
anomaly:
- with space in the dentition;
- without space in the dentition;
- with concomitant anomalies of the
dentition and bite;
- with compensated deficiency of
space in the dentition;
- with decompensated or complete
deficiency of space in the dentition.
Research methods:
1.
Clinical.
2.
Paraclinical.
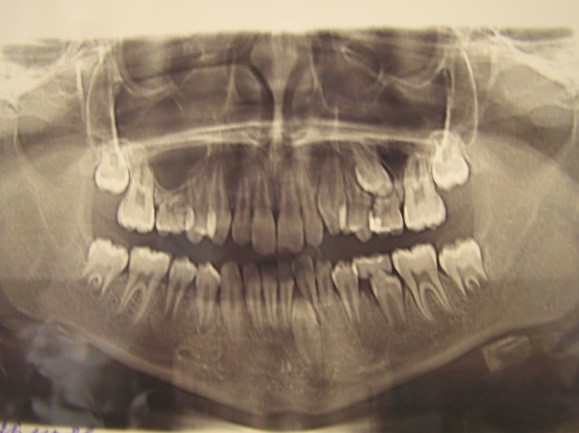
X-ray:
-
orthopantomography;
-
computer tomography.
Biometric:
- dental
examination by methods:
Tonn
Bolton
Pont and
H. Linder, G. Hart
Korkhaus
Snagina
Little
Nance
Schwarz
Fuss
Schmuth
Facial
photometry.
Reopardodontography.
Principles of
treatment:
Preparatory period
-
psychotherapeutic preparation;
- oral
cavity sanitation;
-
checking the state of oral hygiene, if necessary -
training;
-
prosthetic preparation (according to indications);
-
surgical preparation (according to indications);
- if the
transposition of the teeth does not cause functional and aesthetic disorders,
then orthodontic treatment is not indicated. In other cases, therapy is carried
out according to the principle of mesial or distal tooth
movement.
Active
period of orthodontic treatment in temporary and mixed
occlusion:
- functional treatment methods (myogymnastics,
massage, etc.);
- appliances treatment method taking
into account the clinical manifestation of the pathology (creation of space in
the dental arch for an abnormally located tooth: distalization or mesialization
of the teeth, expansion of the dentition, elongation of the
dentition);
- normalization of functions (aesthetic,
chewing).
- stripping.
Active
period of orthodontic treatment in permanent
occlusion:
- appliances treatment method taking
into account the clinical manifestation of the pathology (creation of space in
the dental arch for an abnormally located tooth: distalization or mesialization
of the teeth, expansion of the dentition, elongation of the
dentition);
- normalization of functions (aesthetic,
chewing).
- stripping;
- prosthetic treatment;
- functional treatment methods (myogymnastics,
massage, etc.);
- physiotherapeutic treatment method: vacuum
therapy, low-frequency therapeutic vibration, MRI-magnetic resonance
reflexotherapy, ultraphonophoresis, ultrasound, electrophoresis,
etc.
Retention
period of orthodontic treatment
- preservation of the achieved result and
prevention of relapse using special equipment - retainers (fixed,
removable);
- functional adaptation to the newly created
occlusion;
- extraction of the rudiments of third molars
(if necessary).